Standard Custom Piston Features

- Fully CNC Machined Piston
- Precision Machined CNC
Ring Grooves - 2618 Low-Silicon or optional 4032
High Silicon material available on
some applications
- Diamond Turned Skirts
- Radiused Valve Reliefs
- Single Forced Pin Oilers
- Pick Lock Grooves
(for use with wire locks)
- Machined Side Reliefs on
full round forgings - Lock Grooves Machined for Carbon
Steel Spiro Locks
(other options available) - Engineered for your application!
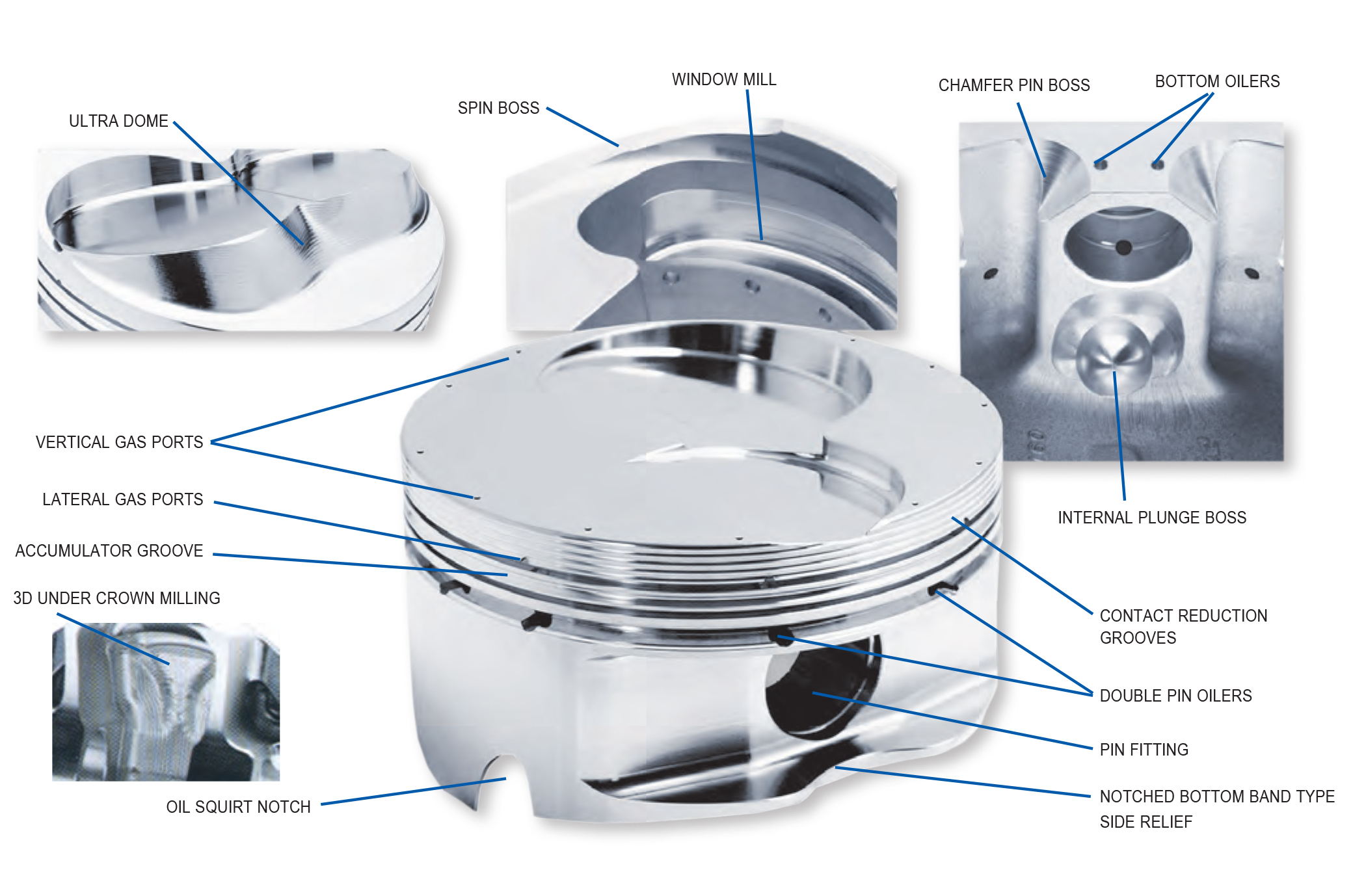
Ultra Crown Dome / Inverted Dome: The Ultra Crown machining process allows incredibly precise dome to cylinder head tolerances. By mapping the exact shape of a piston or cylinder head, optimum compression and quench characteristics can be achieved.
3D Under Crown Milling: The Under Crown machini–ng process allows for uniform deck thickness, therefore creating a lighter and more durable piston.
Vertical Gas Ports: Vertical holes in the deck of the piston, allows combustion pressure to directly enter behind the top ring on the power stroke, thus pressurizing the area behind the top ring for greater ring to cylinder wall seal. During the rest of the cycle, the ring has normal tension for reduced friction. (Most commonly used for drag race applications).
Lateral Gas Ports: This process mills slots into the top of the top ring groove and provides a pathway for combustion pressure to get behind the top ring. This process helps to increase ring seal and is most common in circle track applications.
Ultra Groove: Ultra Groove is a special ring groove machining process that provides near perfect groove flatness and surface finish. Tolerances are held to millionths of an inch.
Pin Boss & Window Milling: In certain applications window milling will remove a significant amount of weight from the skirt of the piston while maintaining its strength and integrity. Spin Boss refers to machining on the bottom of the pin boss, which removes weight where it is not needed for strength.
Plunge Boss & Chamfer Pin Boss: Machining process that removes additional material for added weight savings.
Contact Reduction Grooves: The purpose of machining these grooves is to reduce the amount of contact area against the cylinder wall when the piston “rocks over”. Contact reduction also serves to disrupt the flame travel into the crevice area thus helping to reduce detonation.
Accumulator Grooves: An accumulator groove is machined into the land between the top and second ring. It provides additional volume where residual combustion gases that have “blown by” the top ring can collect. This additional volume helps to reduce pressure between the top & second ring, thus aiding in top ring seal and minimizing ring flutter.
Double Pin Oilers: Double Pin Oilers deliver twice the amount of oil to the wrist pin as compared to the standard single pin oiler.
Pin Fitting: The pin bore is precision honed to attain an exact pin clearance. Clearances typically range from .0003 to .0010 between the wrist pin and pin bore.
Oil Squirt Notch: Notching can be done on pistons for motors with oil squirters, or to avoid contact between pistons and/or pistons and crankshaft.
Bottom Oilers: This process machines one or two holes into the bottom of the pin boss to assist in splash pin lubrication.
Tulip Valve Pockets: Most commonly used on Hemi and motorcycle engines, this process leaves a raised area on plunged valve pockets to achieve maximum compression.
3D Under Crown Milling: The Under Crown machini–ng process allows for uniform deck thickness, therefore creating a lighter and more durable piston.
Vertical Gas Ports: Vertical holes in the deck of the piston, allows combustion pressure to directly enter behind the top ring on the power stroke, thus pressurizing the area behind the top ring for greater ring to cylinder wall seal. During the rest of the cycle, the ring has normal tension for reduced friction. (Most commonly used for drag race applications).
Lateral Gas Ports: This process mills slots into the top of the top ring groove and provides a pathway for combustion pressure to get behind the top ring. This process helps to increase ring seal and is most common in circle track applications.
Ultra Groove: Ultra Groove is a special ring groove machining process that provides near perfect groove flatness and surface finish. Tolerances are held to millionths of an inch.
Pin Boss & Window Milling: In certain applications window milling will remove a significant amount of weight from the skirt of the piston while maintaining its strength and integrity. Spin Boss refers to machining on the bottom of the pin boss, which removes weight where it is not needed for strength.
Plunge Boss & Chamfer Pin Boss: Machining process that removes additional material for added weight savings.
Contact Reduction Grooves: The purpose of machining these grooves is to reduce the amount of contact area against the cylinder wall when the piston “rocks over”. Contact reduction also serves to disrupt the flame travel into the crevice area thus helping to reduce detonation.
Accumulator Grooves: An accumulator groove is machined into the land between the top and second ring. It provides additional volume where residual combustion gases that have “blown by” the top ring can collect. This additional volume helps to reduce pressure between the top & second ring, thus aiding in top ring seal and minimizing ring flutter.
Double Pin Oilers: Double Pin Oilers deliver twice the amount of oil to the wrist pin as compared to the standard single pin oiler.
Pin Fitting: The pin bore is precision honed to attain an exact pin clearance. Clearances typically range from .0003 to .0010 between the wrist pin and pin bore.
Oil Squirt Notch: Notching can be done on pistons for motors with oil squirters, or to avoid contact between pistons and/or pistons and crankshaft.
Bottom Oilers: This process machines one or two holes into the bottom of the pin boss to assist in splash pin lubrication.
Tulip Valve Pockets: Most commonly used on Hemi and motorcycle engines, this process leaves a raised area on plunged valve pockets to achieve maximum compression.
